Dynamic filters
You can use dynamic filters to find data in the global search in a smart way. Dynamic filters connect to multiple entities, like relations, and dynamically offer filter options based on the search results.
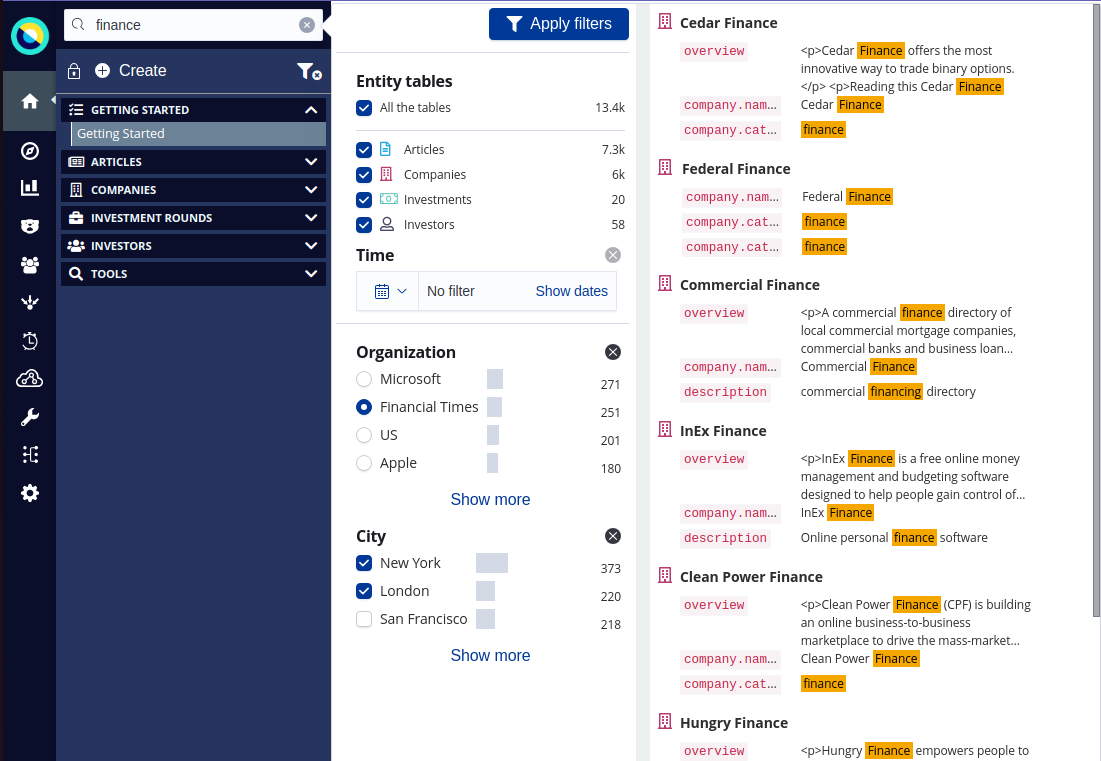
The count of documents related to each option is displayed next to it. Dynamic filters and their options are displayed only if they’re relevant. For example, if you have only the Articles entity table selected, only the dynamic filters that filter articles are displayed.
Creating and mapping dynamic filters
Before you can use a dynamic filter in the global search, you must create it and then map it to an entity table. When you are creating the dynamic filter you must select the filter type and behavior.
Filter type
- Keyword
-
Dynamically filter results based on the keyword values of fields in entity tables. Because your data might have many terms, you must configure this filter with a limit to the number of terms that are provided as options.
- Number
-
Dynamically filter results based on the numeral values of fields in entity tables. When creating this dynamic filter, you define the number ranges that you can filter by in the global search.
- Text
-
Dynamically filter results based on text located anywhere in a text field. By default, the words in your query can be anywhere in the field, but this filter also allows you to search for the words in sequence.
- Date (Age)
-
Dynamically filter results based on age. This is computed based on the mapped date field. When creating this dynamic filter, you can define the age ranges.
- Date
-
Dynamically filter results based on date located in a date field. By default, this filter allows you to search on a specific date or within a date range.
- Any (Exists)
-
Dynamically filter results based on the presence of a field in a document. This determines the existence of a field based on the rules described in the Elasticsearch exists query documentation.
Filter category options
- Automatic
-
This automatically generates the list of categories based on the terms that appear in the results.
- Manual
-
This allows you to manually specify the categories that can be filtered.
- No categories
-
This renders an input field where you manually input the value you are searching for.
Filter behaviors
- Total categories
-
The total amount of categories you want the dynamic filter to have. Larger amounts of categories require more time to generate. Required with Text type filters.
- Initially shown
-
The number of categories you want the filter to display initially in the global search. Entering a smaller number prevents filters taking up too much vertical space. Required for Text type filters.
- Default time range
-
The global search time range defaults to the time range specified by the
timepicker:timeDefaultproperty in Advanced Settings. - Input mask
-
Controls and modifies the user input for dynamic filters that use input fields. For example, if you create a dynamic filter to search for telephones numbers, you can create a mask to ensure that the telephone number is entered in a specific format. Use the following characters to construct the mask:
0 - any digit a - any letter * - any character \ - escape a character, digit or letter [ ] - make input optional { } - include fixed part in unmasked value ` - prevent symbols shift backExamples:

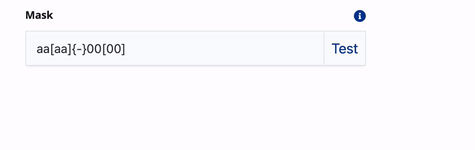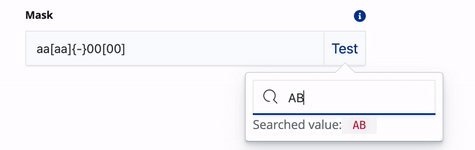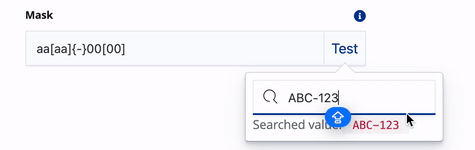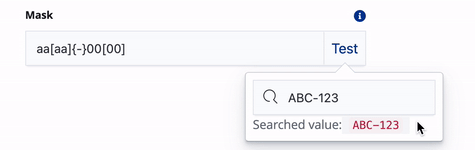
- Date behaviors
-
Date type dynamic filters have the following configuration options:
- Date format
-
You can configure the
dateFormatproperty in Advanced Settings. - Use ranges
-
Determines if your date filter searches on a specific date or within a specified range.
- Include time
-
Determines if your date filter uses hours and minutes, regardless of the configured date format.
- Ignore time zone
-
Determines if your date filter ignores the time zone you are in and performs date queries in Coordinated Universal Time (UTC). When an absolute date is selected, it’s treated as UTC, and when a relative date is selected, it’s relative to the user’s current local time, ignoring the time zone they’re in.
- Partial date matching
-
Date filters that are configured for single date input support wildcard characters. This allows you to search for dates that match your pattern. For example:
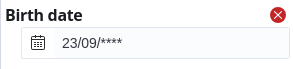
The above input searches for all people born on September 23, of any year. The number of wildcards for each part of the date must fully match the date format:
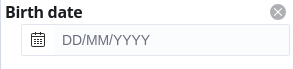
Because of the complexity of these pattern matching queries, wildcards are only supported for date formats that only include
Y,M,D,H,h,mands. Using additional format specifiers, such asw,AandS, disables wildcard support from these filters.
Creating dynamic filters
To create a dynamic filter:
-
Go to the Data model app.
-
Click Dynamic filters and click Create dynamic filter.
-
Enter a name, select the filter type and select the category type.
-
Optional: Depending on the filter type you select, you might need to select the amount of categories to show. See Filter behavior.
-
-
Optional: Turn on Single-selection to allow the selection of only one dynamic filter option at a time in the global search. Turning off single selection allows multiple options. This means that results include documents that match at least one of the options selected.
-
Click Save.
Mapping dynamic filters
Map the dynamic filter to all the entity table fields that you want it to filter on.
-
In the Data model app, select the entity table.
-
Go to the Dynamic filters tab and click Add dynamic filters.
-
Select the dynamic filters and click Add dynamic filters.
-
For each dynamic filter, select the fields to map.
-
From the Options menu, click Save.
-
Repeat the above steps for each entity table.
Using dynamic filters
When a dynamic filter is created and mapped, you can use it in the global search.
-
Go to Dashboard.
-
In the sidebar, enter a search term. The dynamic filters appear as you enter search terms.
-
Select the filter options that you want to filter on.
-
Click Apply filters.
If you select multiple options within one dynamic filter, the results include documents that match at least one of the options selected. If you select options in multiple dynamic filters, the results include only documents that satisfy all filters.